Translating in Excel
Translating the metadata structure into the target language in Excel is quite straightforward. Simply open the XML file in Excel: choose the default settings As an XML table and Excel will create a schema based on the XML source data.
Identifier is the identifier of the concept, i.e. the word or phrase to be translated. For example, an identifier starting with PropertyDef indicates that it is a property definition name. ObjectType is an object type name and UserGroup is a user group name. M-Files creates these identifiers automatically. The translator does not need to pay much attention to these identifiers as such, although they can be helpful pointers when choosing a suitable translation. For a closer look at how the identifiers are named, see Naming convention of the identifiers.
The Source column contains the concepts to be translated. The Target column is empty. The translator enters the translations in this column.
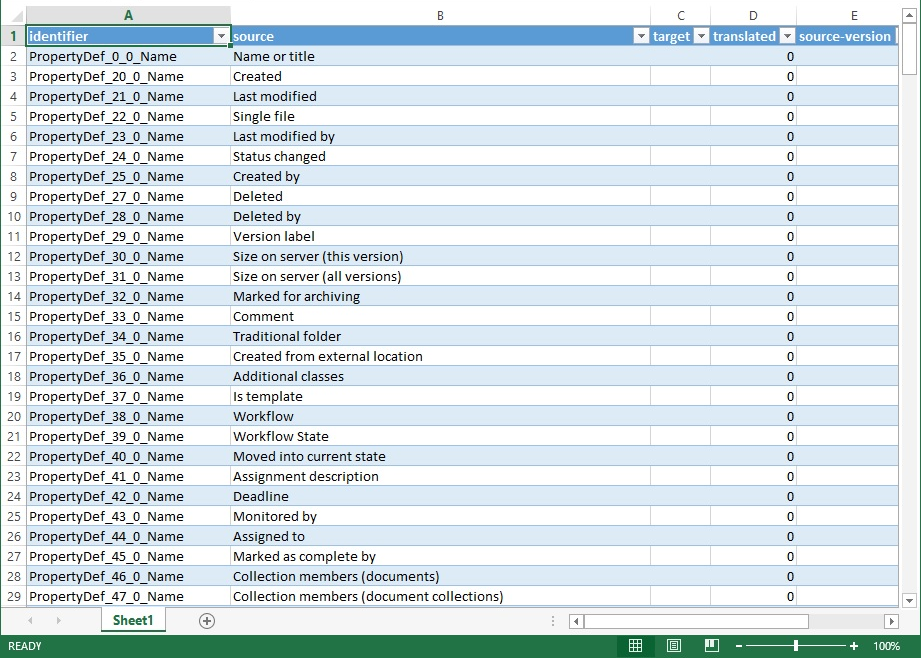
The exported XML table opened in Excel for translation.
In the above example, a translation from English to the target language has been started. The translation for each source language string is to be placed in the target column. When the translation has been added, the 0 in the translated column should be replaced with 1. This tells M-Files that the strings has been translated.
Naming convention of the identifiers
The identifiers are formed as follows: TableID_ResourceID1_ResourceID2_StringID.
- Table ID: Identifies the type of the metadata structure element in question.
- PropertyDef
- ObjectType
- Item (referring to any translatable value list item)
- NamedACL
- View
- Language
- Record ID 1: The ID number of the metadata element in question. For instance, the Document object type has the identifier ObjectType_0_0_Name, where ObjectType is the table ID and the first 0 is the record ID 1. The record ID 2 is always 0 for elements other than Item.
- Record ID 2: The ID number of the item in question. For example, the workflow Processing job applications in the M-Files sample vault has the identifier Item_7_105_Name, where Item is the table ID, 7 the record ID 1, and 105 the record ID 2 identifying the item on the Workflows value list.
- String ID (Name or NamePlural): The part of the identifier that specifies whether the translation should be in the singular or plural form.